- Loose barks, mosses, lichens that are found on the tree must be removed before measuring the diameter over bark.
- Breast Height (BH) should be measured by means of a measuring stick on standing trees at 1.3m or 1.37m (FAO) above the ground level.
- BH should be marked by intersecting vertical and horizontal lines 12 cm long painted with white paint.
- On sloping land, the diameter at BH should be measured on uphill side.
- In case of the tree is leaning, DBH is measured along the tree stem and not vertically, on the side of the lean for trees growing on flat ground and on uphill side, for trees growing on sloping ground.
- BH should be taken at the lowest point above which the buttress formation is not likely to extend.
- When the tree is forked above the BH, it is counted as one tree, but when it is forked below BH, each fork should be treated as though it were a separate tree.
Sunday, July 1, 2018
Rules of the DBH Measurement
Instruments used in Diameter measurement of trees
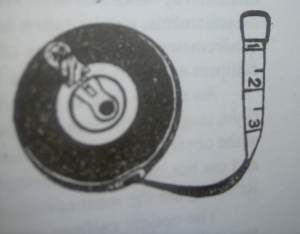
1. Diameter Tape
The Diameter of a tree cross section may be obtained with a flexible tape by measuring the circumference of the tree. A diameter tape is a measuring tape that has scale on both sides: one side is specially marked to show the diameter of a tree, and the other is a normal scale.
2. Calipers
Calipers are often used to measure tree DBHor when diameters are less than about 60cm. A Caliper may be constructed of metal, plastic or wood, consists of a graduated beam with two perpendicular arms. One arm is fixed at the origin of the scale and the other arm slides.When the beam is pressed against the tree and the arms closed, the beam of the Caliper can be read on the scale.

3. Wooden Scale
It is generally a two feet folding scale used to measure diameters of logs at their end cross sections.

The Diameter of a tree cross section may be obtained with a flexible tape by measuring the circumference of the tree. A diameter tape is a measuring tape that has scale on both sides: one side is specially marked to show the diameter of a tree, and the other is a normal scale.

2. Calipers
Calipers are often used to measure tree DBHor when diameters are less than about 60cm. A Caliper may be constructed of metal, plastic or wood, consists of a graduated beam with two perpendicular arms. One arm is fixed at the origin of the scale and the other arm slides.When the beam is pressed against the tree and the arms closed, the beam of the Caliper can be read on the scale.

3. Wooden Scale
It is generally a two feet folding scale used to measure diameters of logs at their end cross sections.

Saturday, June 30, 2018
Silviculture and Silvicultural systems
Silviculture is defined as the art an science of cultivating forest crops. In other words, Silviculture includes both Silvics and its practical application. Silvics is defined as the study of life history and general characteristics of forest crops with particular reference to environmental factors, as the basis for practice of the silviculture.
Objectives of the Study of Silviculture
- Increasing the productivity of the forest
- To fulfill the multifarious requirements of the people with the cultivation of more valuable and useful species of trees
- Improvement of deteriorating natural forest and creating new man-made forest
- Maintaining the good forest condition of both natural and man-made forests by proper tending
A Silvicultural System is defined as a method of silvicultural procedure worked out in accordance with accepted sets of silvicultural principles by which crops constituting forests are tended, harvested and replaced by new crops of distinctive forms.
Silvicultural systems are primarily classified on the basis of the mode of regeneration and this is further classified according to the pattern of felling.
- High Forest Systems- These are the systems in which the regeneration is normally of seedling origin, either natural or artificial or a combination of the both and where the rotation is generally long.
a.Clear -felling System
b. Shelterwood System
c. Selection System
d. High Forest with reserve
e.Two Storeyed High Forest
f .Improvement Felling
2. Coppice Systems- These are those Silvicultural Systems in which the crop originates mainly from coppice and where the rotation of the Coppice is short. These systems are further classified into several Silvicultural systems on the pattern of felling.
a. Simple Coppice system
b.Coppice with Standards system
c. Coppice with reserve System
d. The Coppice of two Rotation system
e.The Coppice Selection system
f.The Shelter wood Coppice System
g. The pollarding
Wednesday, October 4, 2017
Top 10 valuable car brands in the world (2017)
Established in 1916 in Germany the brand has a value of $37.1 billion.
3. Mercedes-Benz
Established in 1926 the German Automaker has a value of $35.5 billion.
4.Volkswagen
Established in 1937 in Germany the brand has a value of 25 billion $.
5.Nissan
1933 Japanese Automaker Nissan is valued 24.8$ billion.
6.Ford
American Automaker Ford is valued 22.4 billion $ in 2017.
7. Honda
1948 Japanese Automaker Honda has seventh place this year with value worth 21.3$ billion.
8.Audi
1909 German Automaker Audi is worth 12.5 $ billion in 2017.
9.Porsche
German Automaker Porsche is valued 12.4$ billion in 2017.
10. Chevrolet
Established in 1911 in America this automaker is valued 11.4$ billion in 2017.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)










